The Backend for AI-Native Applications
Open-source platform for LLM orchestration, multi-agent coordination, and AI-aware observability.
AI isn't just an API call—it's a principal. Symbia treats AI assistants as first-class actors with authentication, authorization, and audit trails, just like human users.
AI is an API call — a stateless function you invoke and forget.
AI is a principal — an actor with identity, state, capabilities, and autonomous action.
Five Problems Symbia Solves
When you add AI to your application, you're adding an actor that can make decisions, take actions, and operate semi-autonomously. Traditional backend architectures weren't designed for this.
Identity Crisis
Who authorized this AI action? Which assistant is executing? What's the audit trail?
Dual Principal Model
Every request carries two authenticated principals: the user who authorized the action AND the assistant executing it. Both are authenticated via JWT, both have declared capabilities, and both are audited.
Orchestration Complexity
AI behavior is complex—routing, branching, fallbacks, tool calls. Imperative code creates tangled state machines.
Graph-Based Workflows
Workflows are declarative JSON DAGs. They're serializable, version-controlled, and runtime-mutable. Design in the visual editor; execute via the Runtime service.
Communication Mismatch
LLM responses stream over seconds. Users interrupt mid-stream. Traditional request/response has no concept of control.
Stream Control Semantics
Every streaming response is controllable via WebSocket control events. Pause it, resume it, preempt it with new context, or hand it off to another assistant.
Observability Gaps
Generic APM doesn't understand tokens, prompt latency, or reasoning chains. Debugging AI requires specialized observability.
LLM-Aware Telemetry
Track logs, metrics, and traces with AI-native awareness. Every LLM call logs prompt tokens, completion tokens, latency, model, and finish reason.
Service Coordination
When multiple AI agents can respond, who goes first? Without coordination, you get race conditions or silence.
SDN with Turn-Taking
Software-Defined Network routes events using explicit contracts. The turn-taking protocol lets agents claim work, defer to others, or observe outcomes.
The Symbia Model
Dual Principal
User + Agent in every request
Entity Directory
UUIDs for all actors (ent_xxx)
Graphs
JSON DAGs, not imperative code
Control Events
pause | resume | preempt | handoff
Turn-Taking
claim → defer → respond
Contracts
Explicit service-to-service auth
The MoltBot Security Reckoning
In January 2026, ClawdBot crossed 60,000+ GitHub stars—then exposed the fundamental fragility of consumer AI infrastructure.
Accessible without authentication via Shodan scans. API keys, OAuth tokens, and conversation histories exposed.
Token Security found ClawdBot running in 22% of customer organizations—without IT approval.
Credentials persisted in plain-text Markdown and JSON. Easy pickings for commodity infostealers.
"A significant gap exists between the consumer enthusiasm for Clawdbot's one-click appeal and the technical expertise needed to operate a secure agentic gateway."
— Eric Schwake, Director of Cybersecurity Strategy, Salt Security
"Clawdbot represents the future of personal AI, but its security posture relies on an outdated model of endpoint trust."
— Hudson Rock Security Assessment
The Root Cause
Bitdefender identified the technical failure: the authentication system automatically approves localhost connections. When deployed behind reverse proxies, all connections appeared to originate from localhost. Every external request was automatically authorized.
This isn't a bug to patch. It's an architecture to replace.
Security by Architecture
Traditional backends treat AI as an integration. Symbia treats AI agents as first-class principals with their own authentication tokens, declared capabilities, audit trails, and access policies.
Credential Routing, Not Storage
MoltBot stores API keys in plaintext files. Symbia never stores credentials locally.
The Integrations Service provides a unified gateway to LLM providers. API keys are fetched on-demand from the Identity Service and held only in memory during request processing.
- Never written to disk
- Never included in logs
- Never exposed through admin interfaces
Multi-Tenant by Default
Every service is designed for multi-tenancy from day one. Data isolation happens at the query layer.
- All requests carry X-Org-Id headers
- Database queries automatically filter by organization
- Cross-tenant access requires explicit super-admin privileges
- Audit logs track all access patterns
Policy-Enforced Networking
The Network Service implements a software-defined networking layer for service mesh operations.
- Contract Enforcement: Services declare what event types they can send and receive
- Policy Engine: Hash-based security with allow/deny/route/transform actions
- Boundary Types: Clear distinctions between intra-sandbox, inter-sandbox, and external communication
The localhost authentication bypass that exposed 1,800+ MoltBot dashboards is architecturally impossible in Symbia.
Token-Based Authentication
RFC 7662-compliant token introspection for service-to-service authentication.
- JWT tokens with short lifespans (15 minutes default)
- Refresh token rotation
- API key management with defined scopes and expiration
- Entitlement-based access for fine-grained permissions
LLM-Native Orchestration
A microservices backend designed from the ground up to manage AI assistants, conversational workflows, and multi-tenant SaaS operations.
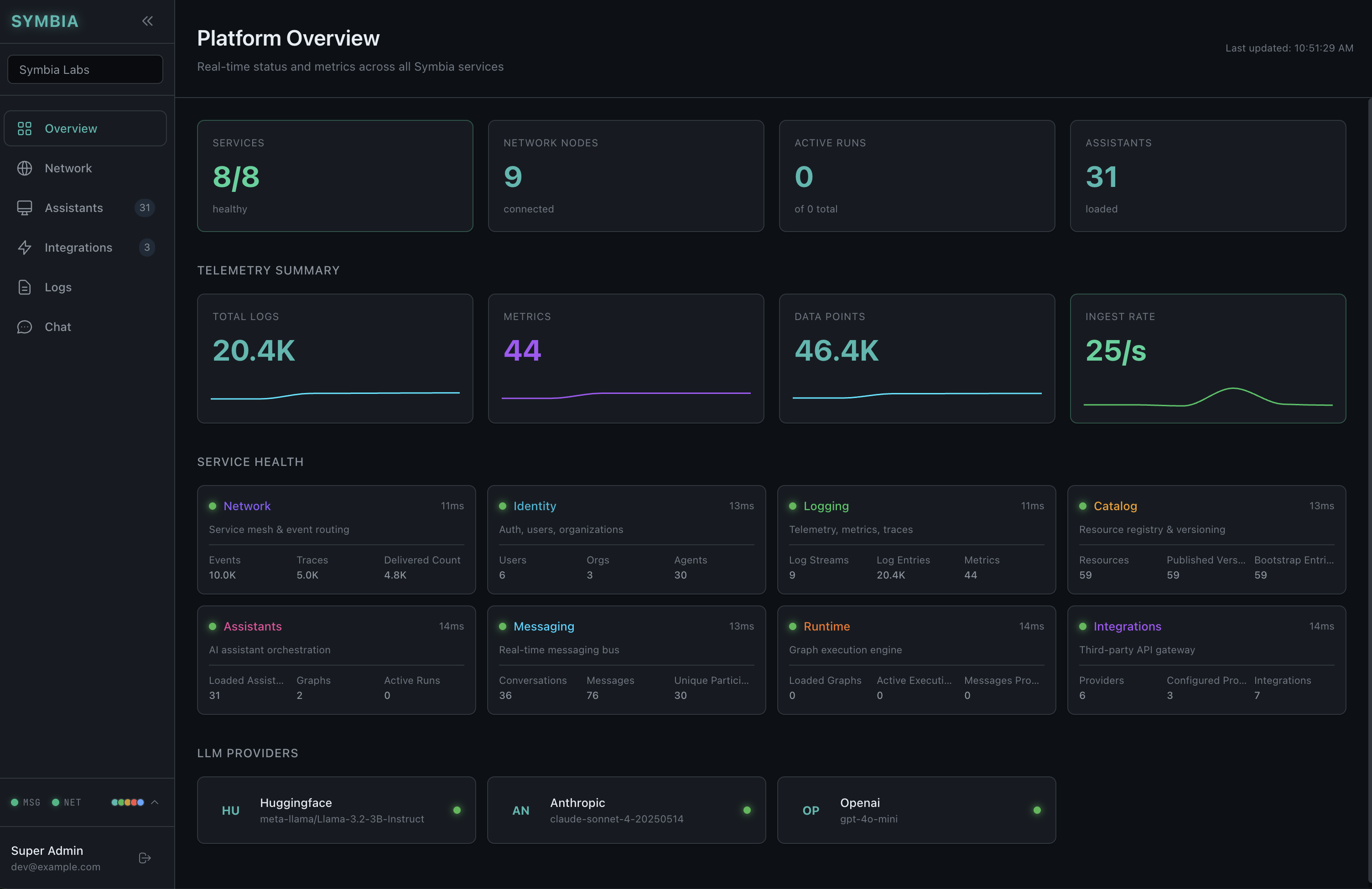
Real-time service health, telemetry, and LLM provider integrations
Identity
Auth, principals, vault
Logging
Logs, metrics, traces
Catalog
Resource registry
Assistants
AI orchestration
Messaging
Real-time comms
Runtime
Graph execution
Integrations
LLM gateway
Network
SDN mesh
Quick Start
Clone & Start
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/symbia-labs/symbia-stack.git
cd symbia-stack
# Start all services with Docker
docker-compose up -dAuthenticate a User
// POST /api/auth/login
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:5001/api/auth/login', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
email: 'user@example.com',
password: 'password123'
})
});
const { token, user } = await response.json();
// token: JWT for subsequent requests
// user: { id, email, orgId, entitlements }Execute an LLM Call
// POST /api/integrations/execute
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:5007/api/integrations/execute', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': `Bearer ${token}`
},
body: JSON.stringify({
provider: 'openai',
operation: 'chat.completions',
params: {
model: 'gpt-4o-mini',
messages: [
{ role: 'system', content: 'You are a helpful assistant.' },
{ role: 'user', content: 'What is Symbia?' }
]
}
})
});
const { data } = await response.json();
console.log(data.content);
console.log(`Tokens used: ${data.usage.totalTokens}`);Send a Real-time Message
import { io } from 'socket.io-client';
const socket = io('http://localhost:5005', {
auth: { token: 'your-jwt-token' }
});
socket.emit('join:conversation', { conversationId: 'conv_123' });
socket.emit('message:send', {
conversationId: 'conv_123',
content: '@logs show me errors from the last hour',
contentType: 'text'
});
socket.on('message:new', (message) => {
console.log('New message:', message.content);
});What Makes Symbia Different
Entity Directory
Unified identity table spanning users, agents, and services. Every entity gets a UUID (ent_xxx) that works across all services.
Turn-Taking Protocol
Multi-agent coordination without race conditions. Agents claim work with explicit justification, defer to others, or observe.
Entitlements Model
Capabilities (cap:*) plus roles (role:*) with inheritance. Fine-grained permissions like cap:messaging.interrupt.
Contract-Based Communication
No implicit service-to-service calls. Every path requires explicit authorization. Audit every event. Enforce policies at the network layer.
Dual-Mode Database
Same code runs on PostgreSQL (production) or pg-mem (development). No Docker required for local dev. npm run dev just works.
Self-Documenting Services
Every service auto-generates /docs/llms.txt — LLM-optimized documentation. Assistants discover capabilities without human help.
Graph-Based Workflow Execution
MoltBot workflows are essentially scripts—linear sequences that fail unpredictably when conditions change. Symbia's Runtime Service executes directed graphs with:
- Topological Ordering — Automatic dependency resolution via Kahn's algorithm
- Parallel Execution — Independent paths run concurrently
- State Persistence — Execution state survives crashes
- Human-in-the-Loop — Human steps are a node type, not an exception
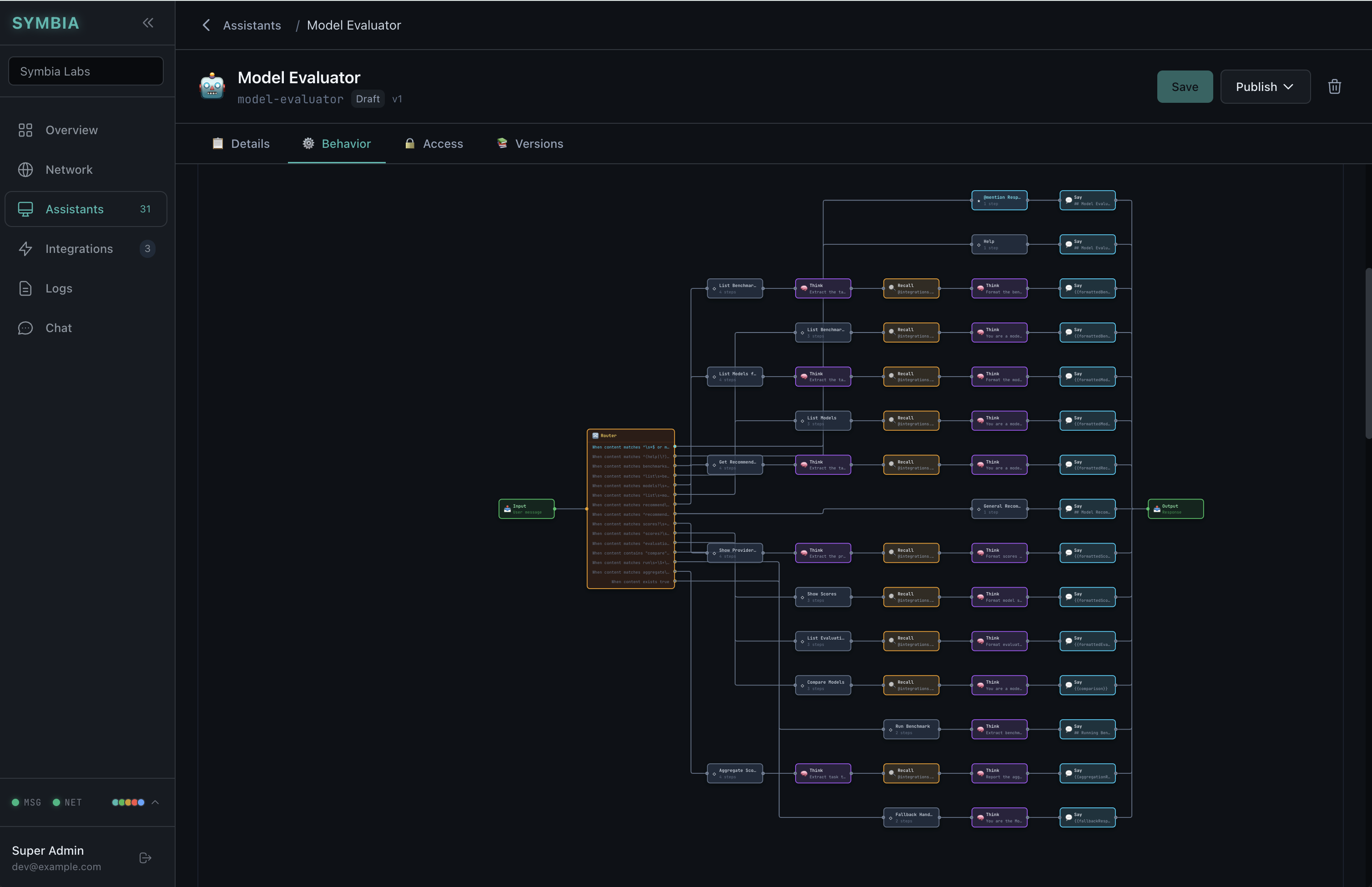
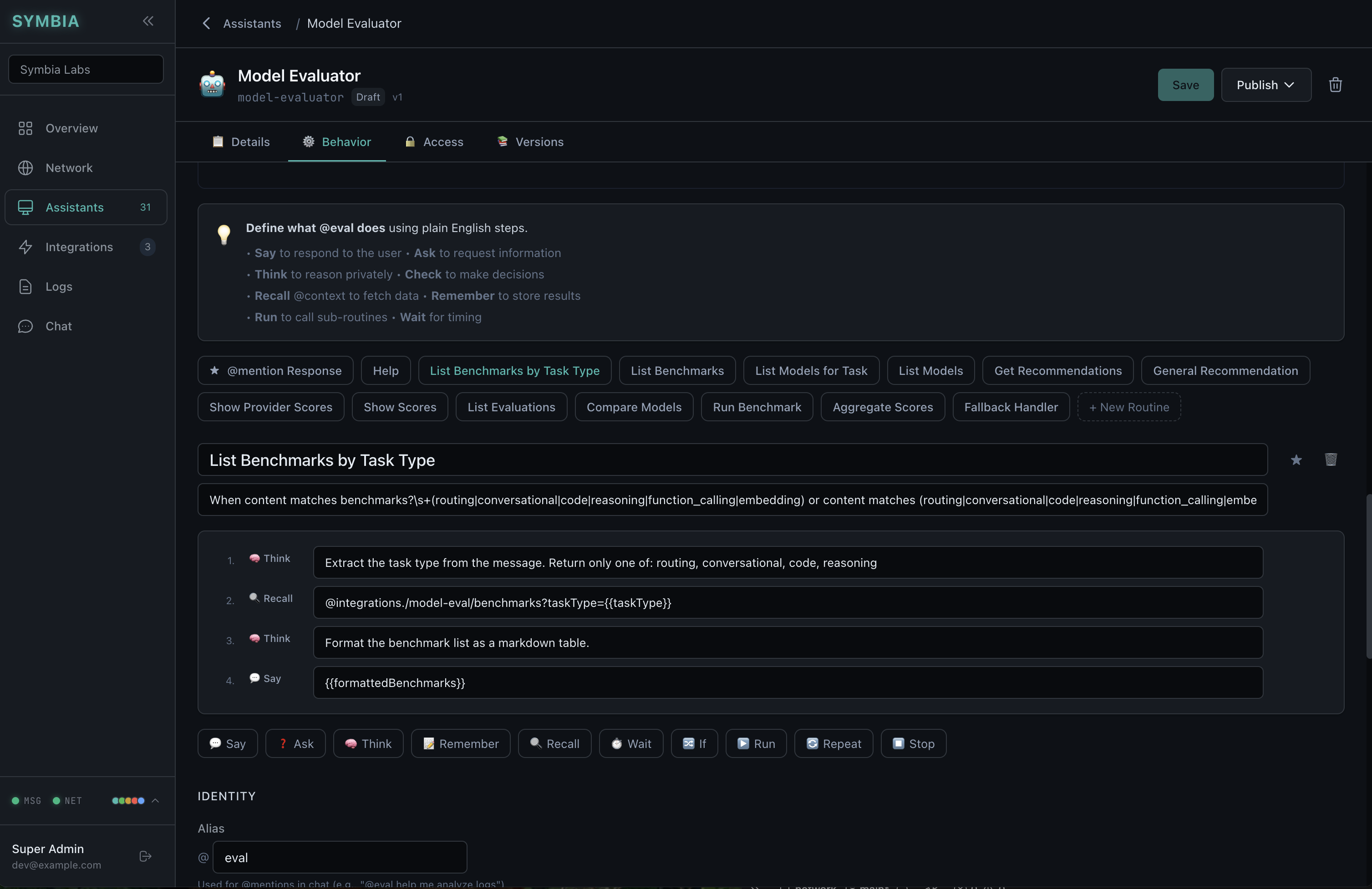
Plain-English Behavior Definition
Define what your AI assistant does using natural language steps:
Say to respond to the user
Think to reason privately
Recall @context to fetch data
Remember to store results
Run to call sub-routines
Rules are inspectable, testable, and logged. Capabilities are explicitly declared and enforced.
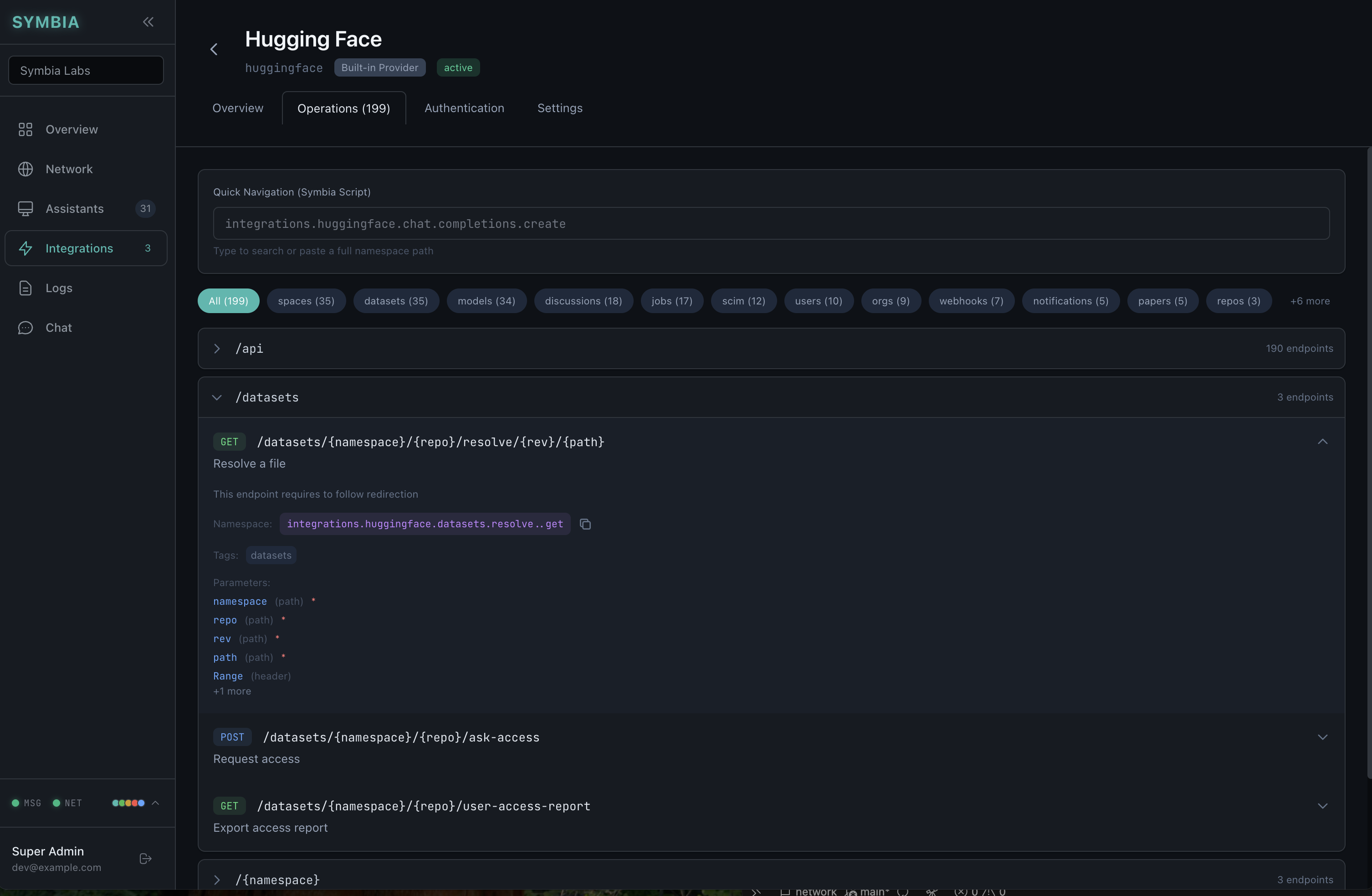
Unified LLM Gateway
MoltBot connects directly to LLM providers, with each installation managing its own credentials. This creates credential sprawl.
Symbia's Integrations Service acts as a unified gateway:
- Multi-Provider Support — OpenAI, Anthropic, HuggingFace with normalized responses
- Response Normalization — Consistent format regardless of provider
- Usage Tracking — Token counts and request metadata for billing
- Credential Routing — API keys fetched from Identity, never stored locally
Latest from Symbia Labs
Why We're Still Rooting for Moltbot
A vision worth saving. The project's collapse was not a failure of its vision—it was a predictable consequence of inadequate infrastructure.
January 2026 Analysis5 Shocking Lessons from the ClawdBot Saga
The AI assistant that took over GitHub—then imploded. From a $16M crypto scam to 1,800+ exposed dashboards and shadow AI in the enterprise.
January 2026 Executive BriefingThe MoltBot AI Agent Security Crisis
Executive summary of the MoltBot phenomenon, security failures, and proposed architectural solutions for enterprise AI infrastructure.
January 2026 ArchitectureAn Architectural Tale of Two AI Agents
A side-by-side comparison of MoltBot vs. Symbia: credential storage vs. routing, shared houses vs. secure apartments, and why security must be foundational.
January 2026 Case StudyThe Rise and Fall of MoltBot
How 60,000+ GitHub stars, 1,800+ exposed dashboards, and a $16M crypto scam revealed the urgent need for secure AI infrastructure.
January 2026 Technical GuideMigrating from MoltBot to Symbia
A comprehensive technical guide to secure AI orchestration. Learn how to convert MoltBot skills to Symbia Assistants with proper identity, policy, and audit capabilities.
January 2026The Path Forward
The MoltBot phenomenon proved that demand for AI agents is real. But it also revealed that shipping powerful capabilities without proper infrastructure creates more problems than it solves.
Symbia represents a different approach: infrastructure designed for the agentic era.
View on GitHubhello@symbialabs.com